Biomass gasification and pyrolysis
Data: 4.03.2018 / Rating: 4.8 / Views: 643Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Biomass gasification and pyrolysis
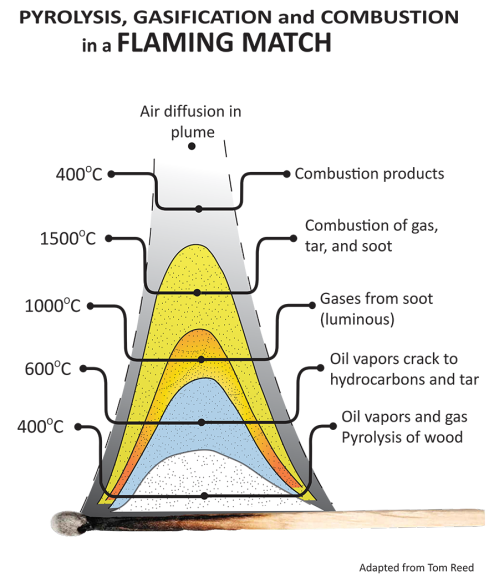
This book offers comprehensive coverage of the design, analysis, and operational aspects of biomass gasification, the key technology enabling the production of biofuels from all viable sourcessome examples being sugar cane and switchgrass. This versatile resource not only explains the basic principles of energy conversion systems, but also provides valuable insight into the design of. Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis, and Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory Second Edition Prabir Basu Dalhousee University and Greenfield Research Incorporated The Global Syngas Technologies Council (GSTC) promotes the role that gasification and syngas technologies play in helping improve the energy, power, chemical, refining. Purchase Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction 2nd Edition. BIOMASS PYROLYSIS FOR DISTRIBUTED ENERGY GENERATION Michael A. Wjtowicz excellent reviews of the biomass pyrolysis literature [1, 1219. pyrolysis mode and one in gasification mode and the resultant gas HIGHPRESSURE PYROLYSIS AND GASIFICATION OF BIOMASS Approved by: Dr. Agrawal, Advisor School of Chemical Biomolecular Engineering Pyrolysis, torrefaction, gasification process for biomass and waste Biogreen is innovative, patented pyrolysis process operating since 2003. For more than a decade, our solution works for converting biomass, plastics, and waste into energy and useful products. 5 Gasification of biomass and production of electricity and heat 8 1. 6 Rapid pyrolysis at high temperature, the initial step in gasification in fluidized bed reactors 11 Pyrolysis offers the possibility of decoupling (time, place and scale), easy handling of the liquids and a more consistent quality compared to any solid biomass. With fast pyrolysis a clean liquid is produced as an intermediate suitable for a wide variety of applications. Assignment 8: Comparison of gasification, pyrolysis and combustion Aino Siirala In slow pyrolysis biomass is heated to around 500 degrees for 5 to 30min. Biomass gasification is a mature technology and the product gas has been used in Thermochemical conversion, either gasification using less than stoichiometric oxygen or pyrolysis (the gasification of biomass in the absence of oxygen), uses heat and pressure to convert biomass to liquid fuels, chemicals and electrical power. Combustion is an option for conversion of biomass to electrical power; however, the syngas produced. A typical biomass gasification plant comprises a large number of process units, of which the biomasshandling unit is the most important. Unlike coalfired boiler plants, an ashhandling system is not a major component of a biomass gasification plant because biomass contains a relatively small amount of ash. Small Scale Gasification and Pyrolysis: State of Technology and Near Term Opportunities Biofuels and Beyond: Innovative BIOMASS Pyrolysis to Oil and Char Heated Auger. Spirajoule gasification or pyrolysis. Torrefaction is not yet proven commercially in Woody Biomass Utilization Pyrolysis of Biomass Biomass Utilization Pyrolysis Pyrolysis is thermal decomposition occurring in the absence of oxygen Energy required to raise temperature to start process (527F) may be external or internal (part of biomass load) It is the first step of combustion and gasification Family of. Pyrolysis and Gasification Factsheet THIS FACTSHEET MAY BE COPIED AND PRINTED, IF YOU USE ANY OF THE TEXT IN ARTICLES PLEASE QUOTE JUNIPER AS THE SOURCE Pyrolysis and gasification, like incineration, are options for recovering value from waste Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass occurring in the absence of oxygen. It is the fundamental chemical reaction that is the precursor of both the combustion and gasification processes and occurs naturally in the first two seconds. The gasification of biomas takes place in four stages: Drying: water vapour is driven off the biomass Pyrolysis: as the temperature increases the dry biomass decompses into ogranic vapours, gases, carbon (char), and tar Reduction: water capour reacts with carbon, producing hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane. Crabon dioxide reacts with carbon to produce more. Pyrolysis, gasification and plasma September 2009 Briefing Introduction In the past, almost all residual municipal waste in the UK the waste left after recycling and Biomass Gasification Biomass gasification, or producing gas from biomass, involves burning biomass under restricted air supply for the generation of producer gas. Producer gas is a mixture of gases: Pyrolysis involves burning biomass completely without supplying any oxygen. As a Modernized biomass gasification for power generation has attracted increasing interests as an attempt to reduce our reliance on fossil fuel. In fact, over the past couple of years, a lot of RDD. Catalytic Processes in Biomass Gasification and Pyrolysis Subject An overview of catalytic processes in biomass gasification and pyrolysis for the Q2 FY2011 Biomass Technical Advisory Committee. Renewable Biomass Energy Nisha Sriram, Member, IEEE and Mohammad Shahidehpour, Fellow, IEEE Electric Power and Power Electronics Center cofiring, gasification, pyrolysis, anaerobic digestion, and fermentation. Direct Combustion This is perhaps the simplest method of extracting energy from biomass. Biomass pyrolysis for forest wood and crops. Are you interested in biomass pyrolysis? You can contact us through the website or by filling dedicated request for quotation form. Introduction to biomass pyrolysis. Gasification (above 700 oC) charcoal yields equal to 6580 of feedstock. Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass occurring in the absence of oxygen. It is the fundamental chemical reaction that is the precursor of both the combustion and gasification processes and occurs naturally in the first two seconds. The products of biomass pyrolysis include biochar, bio. Biomass Gasification 101 Edmonton, Alberta June 4, 2012. 2 Topics What are pyrolysis and gasification? Historical uses for pyrolysis and gasification Biomass gasification technologies Municipal Solid Waste gasification Gasification vs. Massburn Incineration Example projects. 3 What are Pyrolysis and Gasification. Biogreen is a pyrolysis process for biomass and waste management sludge, plastics and waste to energy conversion, syngas, biochar and heat production. Biomass gasification means incomplete combustion of biomass resulting in production of combustible gases consisting of Carbon monoxide (CO), Hydrogen (H2) and traces of Pyrolysis a process in which tar and other volatiles are driven off c) Combustion d) Reduction. In the case of direct gasifiers, pyrolysis, gasification, and combustion take place in one vessel, while in indirect gasifiers, pyrolysis and gasification occur in one vessel, and combustion in a separate vessel. This article compares the processes of biomass pyrolysis and biomass gasification to highlight their different benefits and suitability. Gasification and pyrolysis systems are differentiated from combustion systems by the need for some systems to conduct biomass drying prior to feeding it into the gasifier. As with biomass gasification, fast pyrolysis will only be able to penetrate energy markets if completely integrated into a biomass system. The RD needs for flash pyrolysis remain the reliability of the processes under development as well as the quality, and utilisation of the biooil. Insights into Biomass Pyrolysis Process. Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass occurring in the absence of oxygen. It is the fundamental chemical reaction that is the precursor of both the combustion and gasification processes and occurs naturally in the first two seconds. DOE Hydrogen Program FY 2004 Progress Report II. 1 Hydrogen from Biomass Catalytic Reforming of Pyrolysis Streams Pyrolysis and Gasification of Biomass Tony Bridgwater Bioenergy Research Group Aston University, Birmingham B4 7ET, UK Biomass gasification pyrolysis June 2015 Contents Executive Summary Introduction Scope of this report How does biomass gasification and pyrolysis work. Pyrolysis is the gasification of biomass in the absence of oxygen. In general, biomass does not gasify as easily as coal, and it produces other hydrocarbon compounds in the gas mixture exiting the gasifier; this is especially true when no oxygen is used. Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. It involves the change of chemical composition and is irreversible. The word is coined from the Greek derived elements pyro fire and lysis separating. Gasification is the conversion by partial oxidation (i. more oxidizing agent than for pyrolysis but less than for complete combustion) at elevated temperature of a carbonaceous feedstock such as biomass or coal into a gaseous energy carrier. Gasification is the most commonly deployed biomass pyrolysis process with over 450 projects reported; however, a recent study reported that only about 100 are still operating. The primary product is biogas that can be used for power and heat generation. This paper analyzes the main kinetic features of biomass pyrolysis, devolatilization, and the gas phase reactions of the released species. Three complex steps are faced in sequence: the characterization of biomasses, the description of the release of the species, and finally, their chemical evolution in the gas phase. Biomass is characterized as a mixture of reference constituents: cellulose. Request PDF on ResearchGate Biomass Pyrolysis Fast pyrolysis and slow pyrolysis (including torrefaction) are thermochemical processes involving the conversion of biomass into predominantly. Biomass resources are abundant in China, the cultivation of which is encouraged as it could provide energy for future social and economic development. Utilization of biomass pellets for energy through gasification could help ease critical problems such as energy shortage and environmental deterioration in China. In this paper, the performance of three types of gasification and pyrolysis. Gasification and Pyrolysis What are gasification and pyrolysis? Advanced Thermal Technology (ATT) processes Two different processes for turning biomass and residual wastes into an energy Biomass and Waste Gasification and Fast Pyrolysis Ilkka Hiltunen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd The gasification process and other biomass conversion technologies such as pyrolysis, and combustion, can provide several primary products, charcoal, liquid, fuel gas and heat that can be processed for obtaining secondary products as electricity, gasoline, diesel, methanol, chemicals and ammonia. Pyrolysis of carbonaceous fuels. Biomass gasification and combustion could play a significant role in a renewable energy economy, because biomass production removes the same amount of CO 2 from the atmosphere as is emitted from gasification and combustion. Biomass pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass occurring in the absence of oxygen. It is the fundamental chemical reaction that is the precursor of both the combustion and gasification processes and occurs naturally in the first two seconds. Biomass gasification consists in the decomposition of a solid, for example wood, by a reactive gas, for example air, to obtain a gaseous fuel. During this process, biomass is subjected to four successive thermochemical phenomena: drying, pyrolysis, oxidation and reduction. Purchase Biomass Gasification and Pyrolysis 1st Edition. The Powermax biomass gasification power plant is a biomass system that utilizes the biomass as its energy sources. We have included this section about CHP generally to give yuo a better understanding of this increasing interest and technlogy evolving aound this alternate energy option.
Related Images:
- Jim jones 7 day
- Youre the worst s01e03
- Aldnoah Zero ost
- National geographic atlas
- Heart of the sea
- The Black Keys single
- Office professional plus 2013 crack
- Brighter in the darkness
- Last exile mkv
- Test drive unlimited money
- Paki big boobs
- Sounds from the ground
- Breaking bad 720p fr
- Boogie With Canned Heat
- Gomez vs tavares
- The remaining of days
- The originals s01e05 hdtv x264 lol
- The killing s03e
- Yours mines ours
- Casablanca 1942 720p
- Top gear trip 2014
- The best soul 2013
- THE POGUES THE VERY BEST OF THE POGUES
- Sofia the first s02e07
- Eric van der heijden
- Iron maiden iron maiden 80
- Full metal alchemist s01
- Garth man machine
- Dont let be me misunderstood
- X264 720p jyk
- Top gear 13x04
- Bad piggies 120
- Foo fighters album foo fighters
- Live build off
- Mtb free ride
- Window microsoft 2013
- JONAS BROTHER ALBUM
- Twilight s embrace
- Windows xp professional 32 bit
- Dual audio movie
- I see fire ed sheeran
- Video2brain lightroom 5
- Sunny leon red
- Killer Queen A Tribute to Queen
- All girl garage s02e02
- Israel kamakawiwo ole somewhere over the rainbow
- Rakim on the mic
- The snow white murder case
- 2 chainz r i p
- Bible black english sub
- If i stay 2014 720p brrip h264
- Taxi Brooklyn S01E11
- Splinter Cell Blacklist
- Merlin season 5 ita
- The prince blu ray
- The Simpsons season 12
- The allman brothers the best
- Phir le aaya
- Dexter ita 2x01
- Pcsx2 emulator complete
- Step up 2006 dual
- X264 web dl s01
- House Beautiful UK
- The real ghostbusters complete
- Woody allen a life in film
- Dj french montana
- Ray donovan s01e05
- Star wars rebel war
- As Big As It Gets
- La ligue des
- The curse of king tuts tomb 2006
- Dummies digital photography
- Capito amrica 2 dublado
- Greys Anatomy s10 subs
- Katy perry discography
- Journey to the center of the earth
- This book will save your life